According to the definition provided by the Apprentices Act of 1961, an “apprentice” is a person who is undergoing training as a result of an apprenticeship contract. Under a contract of apprenticeship, “apprenticeship training” is a course of training in any industry or establishment under prescribed terms and conditions, which may vary for different categories of apprentices. Apprenticeship training is a course of training in an industry or establishment that consists of:
- a) A component of basic training;
- b) On-the-job training (OJT) or practical training at work.
The Act mandates the provision of Apprenticeship Training Programs in all industries, including manufacturing and service, if businesses with 30 or more regular and contract employees are required to enroll between 2% and 15% of their workforce (including direct contractual employees) annually. It is permissible to employ apprentices up to a total of 29 workers, but not more than three.
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) is an initiative of the Indian government that aims to provide establishments that are undergoing apprenticeship training with financial support. NAPS went live on August 19, 2016.
Objectives of NAPS
- To promote apprenticeship training in the country.
- To provide financial support to establishments to take up apprenticeship programs in the following ways –
- To support establishments, particularly MSMEs, in engaging apprentices in accordance with the Apprentices Act and paying stipends to them in accordance with prescribed rates; under NAPS, 25% of prescribed stipend is subject to a maximum of Rs. The Indian government provides these establishments with a reimbursement of 1500 INR per apprentice per month in order to hire apprentices.
- To assist businesses, particularly micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), that do not have in-house Basic Training Facilities in order to establish such facilities or to hire Training Partners to carry out the activity on their behalf for new apprentices who must complete such Basic Training prior to joining the shop floor (on-the-job training) under the Apprenticeship program. The cost of basic training is limited to Rs. They are reimbursed 7500/- for a maximum of 500 hours (to be calculated at Rs. 15/hour) or to the Basic Training Provider that the Government of India has hired for them under NAPS.
Basic Training
The theoretical and practical/laboratory instruction sections of each Apprenticeship Programs syllabus are basic training, which includes on-the-job training for apprentices. For those who have not completed any formal or skill-based training prior to beginning on-the-job training or practical training, basic training is an essential part of apprenticeship training. Before moving to the shop floor or work area for practical or on-the-job training, new apprentices receive Basic Training to develop a reasonable level of independence in handling instruments, machinery, and equipment. Note: During basic training, the establishment must pay the apprentice half of the required stipend.
ITI/Graduates/ Diploma holders/Pursuing graduation/Diplomas are exempted from Basic Training excluded Fresh Apprentices. Basic Training usually accounts for 20-25% of the duration of the overall Apprenticeship Program but can vary depending on the specific requirement of the curriculum.
On-the-job-training (OJT)
OJT is training that is done in the real world at a company’s place of business.
Kinds of Trades /Courses
The Apprenticeship Act of 1961 defines two types of trades: designated trades and general trades. The government notifies so-called “Designated Trades“. The other trades that have chosen to be taught by an establishment under the Apprentices Act but are not on the notified list of the Designated Trades is “Optional Trades.“
Eligibility to be apprentices under the Act
Apprenticeship training is open to anyone who is at least 14 years old (or older in the case of hazardous industries as defined by the Apprenticeship Rules), has a minimum of a 5th class pass (for Optional Trade), meets the physical fitness requirements for the course, and holds the minimum educational qualification required for a trade. Please refer to the 2019 Rules and the Apprentices (Amendment) Act of 2014.
Procedure for registration of candidate
The candidate can sign up for an apprenticeship program in a field or trade of his or her choosing by going to the apprenticeship portal:
Do a search for potential employers and apprenticeship opportunities on the apprenticeship portal;
Send applications to the potential employers for the apprenticeship training;
Receive offer letters from establishments online and send his or her acceptance;
Sign the apprenticeship contract with the establishment and begin the apprenticeship program.
Commencement of apprenticeship
The apprenticeship will begin on the date that the apprenticeship contract between the employer and apprentice is signed and registered online. Contracts of apprenticeship must be registered online for both Optional Trades and Designated Trades.
Benefits for employers
Employers who are registered under the Apprentices Act of 1961 are exempt from paying EPF and ESI contributions for apprentices they hire. If they choose NAPS and meet the conditions outlined in it, they can receive financial assistance as described elsewhere in this document. Beyond what is required by the Apprentices Act, businesses that employ apprentices can also use their CSR funds to provide “skill training.”
In accordance with Section 18 of the Apprentices Act of 1961, any apprentice undergoing training in a designated or optional trade in an establishment is considered a trainee and not a worker, and any labor-related laws do not apply to or relate to such an apprentice.
Stipend
The education qualification of apprentices or the education qualification specified in the curriculum will be considered for payment of the minimum stipend amount for skill certified candidates. According to the main rules of the 2019 Apprenticeship Rules, the minimum monthly stipend for apprentices must be based on the curriculum’s requirements. Apprentices will receive a stipend at the following minimum monthly rate:
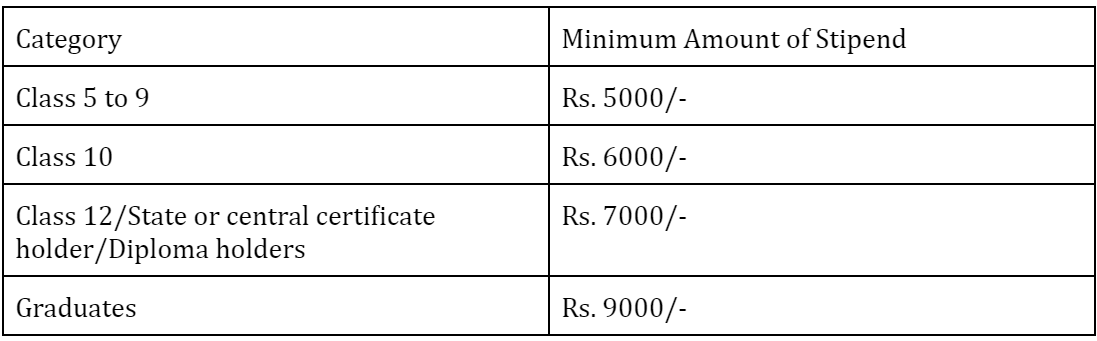
“The education qualification specified in the curriculum shall be the minimum rate of stipend payable to skill certified apprentices per month.”





